
The diesel engine timeline is a long history.
Most automobiles out on the road today run on unleaded gasoline.
But most of the trucks that are responsible for moving freight/products from point A to point B are assembled with diesel engines at the heart of the vehicle.
If you want to know the diesel engine timeline you have to know the creator of these engines first.
His name was Rudolf Diesel.
Who invented the first diesel engine?
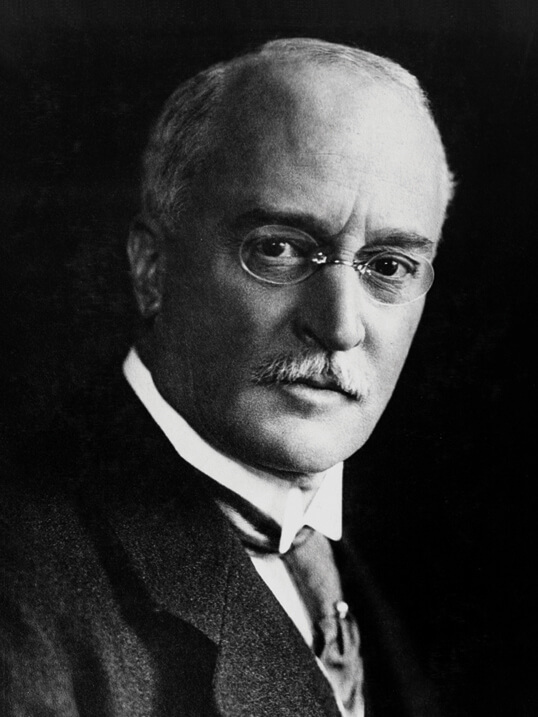
Rudolf Diesel was born in Paris, a city where his family had emigrated from Germany.
He studied in England and subsequently graduated as an engineer at the Polytechnic of Munich,
where he was a disciple of the inventor of the refrigerator, Carl von Linde, for whose company he later worked as an employee.
From 1893 to 1897 he worked for the German group Krupp, specifically in the prestigious company
MAN AG which at that time was already engaged in manufacturing engines.
Rudolf Diesel considered himself a social theorist.
He wrote a work that gathered his vision of the company, Solidarismus. However, his contribution to this field had little impact.
The night of September 29 to 30, while he was aboard a ship from Antwerp to England, disappeared.
Nobody knows with certainty what happened:
only that, a few days later, the coast guard found his body lifeless.
There has been much speculation about the possible cause of his death:
suicide, since according to some sources he was bankrupt;
an accident on the deck due to dizziness caused by frequent headaches,
and even murder for economic interests, since its engine, not requiring the burning of coal, severely affected the industrialists of this sector.
When was the first diesel engine invented
Diesel-2 In his spare time Diesel worked on the development of an engine that was more efficient than those that existed at the time,
which required externally applying the ignition to the internal mixture of air and fuel.
Diesel got the ignition to occur internally:
compressing the air inside the cylinder and heating it in such a way that the fuel,
which comes into contact with the air just before the end of the compression period, ignites itself.
In 1892 he finished his design and a year later he received the patent of the engine that bears his name.
Their contribution was enormous advantages: smaller and lighter engines than those existing to date,
regardless of the fact that they did not require the use of an additional source of fuel for ignition.
Also, its engine ran with a theoretical efficiency of 75% compared to 10% achieved by traditional steam engines, which reduced costs.
Diesel quickly made a lot of money with its patent:
The industry immediately used its engine to power cars, trucks, and ships, electrical pipes, electric power plants, etc.
Current diesel engines continue to be based primarily on their original invention.
Here are some notable moments of the Diesel Engine timeline:
- October 29th, 1897 Rudolf obtains a patent on supercharging the Diesel engine”
- 1899 First two-stroke Diesel engine was built by Hugo Guldner
- 1903 Two first ‘Diesel-powered’ ships are launched.
- 1909 Prosper L’Orange applies for a patent on ‘precombustion chamber injection’
- 1912 The first locomotive with a Diesel engine is used in Switzerland.
- 1913 Commercial ships and US Navy Submarines began to use the diesel engines.
- 1929 First passenger car with a Diesel engine appears on the road.
- 1938 General Motors forms the ‘GM Diesel Division’ which later becomes Detroit Diesel.
- 1946 Clessie Cummins obtains a patent for ‘fuel feeding and injection apparatus for oil-burning engines’ that incorporated a separated pressure generation apparatus and injection timing device.
- 1962-65 Jacobs Manufacturing Company developed/manufactured a “Diesel compression braking system”.
- 1976 Development of the ‘common rail injection’ begins in Zurich.
- 1979 Daimler-Benz produces the first passenger cars with a ‘turbocharged Diesel engine’.
Today, more than 95% of all large heavy-duty trucks use a diesel engine, as is a majority of medium-duty trucks.
Diesel engines are also used in many different areas
– stand-alone generators, marine applications, locomotive industry and construction industry to name a few.
If you are looking for a reliable diesel engine parts supplier, you can contact us or visit our parts page and look for what you need.
Also, if you have the part number, you can do a part search on the “Seach Parts Button” on the top of the website.





